![[Linux] rsyslogd, auditd를 이용한 로그 전송 프로세스 구성](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdna%2Fb9LYSc%2FbtsQMIVMYCQ%2FAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAG1JSgh_yA5OYOCvlBUS3fw_mnpm_KkpRk_Fge2dNO7z%2Fimg.png%3Fcredential%3DyqXZFxpELC7KVnFOS48ylbz2pIh7yKj8%26expires%3D1772290799%26allow_ip%3D%26allow_referer%3D%26signature%3DFHE7W2Ql%252F%252FxaYC5IQ6F16dsAihY%253D)

1. 서버 로깅 구축 관련 개념
Rocky8/9 버전에서 서버에서 발생하는 시스템/서비스/보안 로그의 출처와 포맷이 모두 상이하여 SIEM에서 수집 및 경보화 하기 어려워서 서버 한곳에서 수집한 후 표준 필드로 가공하여 동일 포맷(JSON)로 SIEM에 저장하기 위해 프로세스를 구성하였다.
1) 수집 범위
① SSH 접근/세션 이벤트 수집
성공/실패/잘못된 계정/연결 해제 등 sshd 로그
출발지 IP, 목적지 IP, 출발지 Port, 목적지 Port, 상태 값 출력
② 인증 계정 관련 이벤트 수집 (PAM/login 로그)
su, sudo, login등 인증 세션 시작/종료 ,실패 로그
③ 사용자 입력 명령 이벤트 수집
사용자가 프롬포트에서 입력한 최종 커맨드 저장 (usercmd 채널로 표준화 수행)
④ auditd 이벤트 수집
네트워크 행위: socket/connect/accept/bind(IPv4), 성공/실패
사용자 세션 이벤트
⑤ 시스템/서비스 운용 이벤트 수집
systemd, NetworkManager, cron ,kernel 로그
2) 프로세스 구성도
사용자 입력 명령어, SSH, 커널 및 시스템 서비스 로그가 journald에 저장되며 rsyslog를 통해 가공되어 SIEM으로 전송된다.

rsyslog의 경우 rsyslog.d 하위 폴더에 다수의 conf 파일을 구성 하였으며 동작은 prefix(00~90)가 낮은게 높은 우선순위로 실행된다.
3) 디렉토리 구성도
/etc/rsyslog.d/
00-json.tpl.conf # 출력 포맷(JSON)
00-origin.conf # origin(서버IP) 고정 변수
12-sshd-extract.conf # ssh 로그에서 s_info/d_info 추출
13-usercmd-extract.conf # usercmd 라인에서 s_info/d_info/cmd 추출
20-audit-net-extract.conf # audit(local2) 네트워크 이벤트에서 s_info/d_info 추출
90-out.conf # syslog 전송(UDP)
/etc/profile.d/
99-zz-cmdlog.sh
2. 사전 구성
1) audit, rsyslog 설치
로그를 수집하기 위해 audit, rsyslog를 설치 한다.
sudo dnf -y install rsyslog audit audit-libs
sudo systemctl enable --now rsyslog auditd
커널에 audit 켜졌는지 확인
sudo auditctl -s | egrep 'enabled|backlog_limit'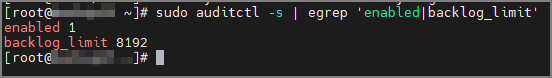
2) audit에서 syslog 플러그인 활성화
sudo tee /etc/audit/plugins.d/syslog.conf >/dev/null <<'EOF'
active = yes
direction = out
path = builtin_syslog
type = builtin
args = LOG_INFO LOG_LOCAL2
format = string
EOF
# 룰 활성화
sudo augenrules --load 2>/dev/null || true
2. rsyslog 파일 구성 방법
1) 00-json.tpl.conf
로그 포맷을 설정하는 파일이다.
로그는 json으로 저장하며 "key: value" 형태로 저장하도록 구성 하였다.
출발지, 목적지 IP/Port 및 상태 값은 네트워크, SSH로그에서만 구성되도록 설정 하였다.
kvQuoteFmt: json 템플릿 명
eventtime: 로그 기록 시간 (RFC3339 timestamp)
originname: 장비 hostname
origin: 장비 IP
s_info: 출발지 IP
s_port: 출발지 Port
d_info: 목적지 IP
d_port: 목적지 Port
status: 상태
app: 프로세스 이름
cmd: 사용자 명령어 입력 값
msg: 로그 전체 내용 (rawdata)
template(name="kvQuoteFmt" type="list") {
constant(value="\"eventtime: ") property(name="timereported" dateFormat="rfc3339")
constant(value="\" \"originname: ") property(name="hostname")
constant(value="\" \"origin: ") property(name="$!origin")
constant(value="\" \"s_info: ") property(name="$!s_info")
constant(value="\" \"d_info: ") property(name="$!d_info")
constant(value="\" \"app: ") property(name="programname")
constant(value="\" \"cmd: ") property(name="$!cmd")
constant(value="\" \"msg: ") property(name="msg" format="json")
constant(value="\"")
constant(value="\n")
로그 출력 예시는 아래와 같다.
"eventtime: 2025-09-24T09:00:12+09:00" "originname: Server1" "origin: 192.168.0.1" "s_info: 192.168.0.100" "d_info: 192.168.0.1" "app: usercmd" "cmd: rm -rf aa" "msg: user=root src=192.168.0.100 dst=192.168.0.1 tty=pts/5 cmd=rm -rf aa"
2) 00-origin.conf
journald/sshd/auditd에서는 목적지 IP가 로그에 찍히지 않기 때문에 로그 발생 시 목적지 IP를 수동 매핑한다.
set $!originip = "[적용할 서버 IP]";
3) 12-sshd-extract.conf
SSH 접근 시 출발지, 목적지 IP/PORT, 상태 값 정보를 추출한다.
접근 로그를 확인 후 22번 이외의 포트로 접근 되는게 확인되면 해당 커스텀 포트로 등록되며 없을경우 기본 22번 포트로 기록된다.
# 선택: 호스트 기본 SSH 포트(없으면 22)
set $.sshd_port = "22";
if ($programname == "sshd" or $msg contains "sshd[") then {
# src IP / src port
set $!s_info = re_extract($msg, "from ([0-9A-Fa-f:.]+) port ([0-9]{1,5})", 0, 1, "");
set $!sport = re_extract($msg, "from [0-9A-Fa-f:.]+ port ([0-9]{1,5})", 0, 1, "");
# dst IP / dst port
set $!d_info = $!origin;
set $!dport = re_extract($msg, " on [0-9A-Fa-f:.]+ port ([0-9]{1,5})", 0, 1, "");
if $!dport == "" then set $!dport = $.sshd_port;
set $!proto = "tcp";
if $msg contains "Accepted " then set $!status = "accepted";
else if $msg contains "Failed " then set $!status = "failed";
else if $msg contains "Invalid user" then set $!status = "invalid";
else if $msg contains "Disconnected" then set $!status = "disconnected";
else set $!status = "";
}
원본로그 출력 값: sshd[497296]: Accepted password for user1 from 192.168.0.100 port 65416 ssh2
추출 값: s_info=192.168.0.100, d_info=192.168.0.1
4) 13-usercmd-extract.conf
/etc/profile.d/99-zz-cmdlog.sh를 통해 출력된 로그에서 src/dst/cmd필드를 추출한다.
# usercmd 라인에서 s_info/d_info/cmd 추출 (추출만)
if $programname == "usercmd" then {
# s_info: IP 우선, 없으면 계정명
set $!s_info = re_extract($msg, " src=([^ ]*)", 0, 1, "");
if $!s_info == "" then
set $!s_info = re_extract($msg, "user=([^ ]+)", 0, 1, "");
# d_info: 명령 실행된 호스트(로컬)
set $!d_info = re_extract($msg, " dst=([^ ]*)", 0, 1, "");
if $!d_info == "" then set $!d_info = $!origin;
# cmd: 공백 포함 끝까지
set $!cmd = re_extract($msg, " cmd=(.*)", 0, 1, "");
}
원본로그 출력 값 user=root src=192.168.123.120 dst=172.31.201.100 tty=/dev/pts/5 cmd=ls -l
추출 값 : s_info=192.168.0.100, d_info=192.168.0.1 , cmd=ls -l
5) 20-audit-usercmd.conf
auditd에서 전송한 네트워크 관련 이벤트에서 출발지, 목적지 IP/PORT, 상태 값를 s_info / d_info/s_port/d_port/status로 매핑한다.
# 20-audit-net-extract.conf
if $syslogfacility-text == "local2" then {
# 예: SADDR={ saddr_fam=inet src=1.2.3.4 sport=5555 dst=5.6.7.8 dport=22 proto=tcp }
set $!s_info = re_extract($msg, " src=([0-9A-Fa-f:.]+)", 0, 1, "");
if $!s_info == "" then set $!s_info = re_extract($msg, "SRC=([0-9.]+)", 0, 1, "");
set $!d_info = re_extract($msg, " dst=([0-9A-Fa-f:.]+)", 0, 1, "");
if $!d_info == "" then set $!d_info = re_extract($msg, "DST=([0-9.]+)", 0, 1, "");
set $!sport = re_extract($msg, " sport=([0-9]+)", 0, 1, "");
if $!sport == "" then set $!sport = re_extract($msg, "SPT=([0-9]+)", 0, 1, "");
set $!dport = re_extract($msg, " dport=([0-9]+)", 0, 1, "");
if $!dport == "" then set $!dport = re_extract($msg, "DPT=([0-9]+)", 0, 1, "");
set $!proto = re_extract($msg, " proto=([a-z0-9A-Z]+)", 0, 1, "");
if $!proto == "" then set $!proto = re_extract($msg, "PROTO=([a-z0-9A-Z]+)", 0, 1, "");
if $msg contains " saddr_fam=local" then set $!proto = "unix";
# 성공/실패는 SYSCALL 라인의 success= 로 판별 (있으면 덮어씀)
set $!status = re_extract($msg, " success=(yes|no)", 0, 1, "");
if $!status == "" then set $!status = re_extract($msg, " result=(success|fail|denied)", 0, 1, "");
}
6) 90-out.conf
출력된 로그를 외부 장비에 syslog로 전송한다.
action(
type="omfwd"
target="[syslog 전송 서버 IP]"
port="514"
protocol="udp"
template="kvQuoteFmt"
)
3. 사용자 명령 수집 스크립트
사용자가 프롬포트에서 친 명령어를 수집하기 위한 스크립트이다.
# /etc/profile.d/99-zz-cmdlog.sh
[[ $- != *i* ]] && return 0
__CMDLOG_READY=0
__CMDLOG_LAST=""
__CMDLOG_LAST_SRC=""
__cmdlog_mark_ready() { __CMDLOG_READY=1; }
__cmdlog_should_skip() {
local c="$1"
[[ -z "${c//[[:space:]]/}" ]] && return 0
[[ $__CMDLOG_READY -ne 1 ]] && return 0
# 예외처리
[[ "$c" == "for i in /etc/profile.d/"* ]] && return 0
[[ "$c" == ". /etc/bashrc"* || "$c" == ". ~/.bashrc"* || "$c" == '. "$i"'* ]] && return 0
[[ "$c" == "[ -r \"$i\" ]"* || "$c" == "unset i"* ]] && return 0
[[ "$c" == "TMOUT="* || "$c" == "export TMOUT"* ]] && return 0
[[ "$c" == "printf \"\\033]0;"* ]] && return 0
[[ "$c" == "[ \"\${-#*i}\" != \"\$-\" ]"* ]] && return 0
[[ "$c" == "__cmdlog_postexec" ]] && return 0
return 1
}
__cmdlog_preexec() {
local c="$BASH_COMMAND" tty src dst spt dpt
tty="$(/usr/bin/tty 2>/dev/null | sed 's#/dev/##')"
if [[ -n "$SSH_CONNECTION" ]]; then
# 4개 필드추출: src_ip src_port dst_ip dst_port
read -r src spt dst dpt <<<"$SSH_CONNECTION"
else
src=""
spt=""
dst="$(hostname -I 2>/dev/null | awk '{print $1}')"
dpt=""
fi
__cmdlog_should_skip "$c" && return 0
if [[ "$c" == "$__CMDLOG_LAST" && "$src" == "$__CMDLOG_LAST_SRC" ]]; then
return 0
fi
__CMDLOG_LAST="$c"
__CMDLOG_LAST_SRC="$src"
logger -t usercmd -- "user=$USER src=$src s_port=$spt dst=$dst dport=$dpt tty=$tty cmd=$c"
}
# 프롬프트 그려지면 이후부터 기록
if [[ -n "$PROMPT_COMMAND" ]]; then
PROMPT_COMMAND="__cmdlog_mark_ready; $PROMPT_COMMAND"
else
PROMPT_COMMAND="__cmdlog_mark_ready"
fi
old=$(trap -p DEBUG | sed -n "s/^trap -- '\(.*\)' DEBUG$/\1/p")
if [[ -n "$old" ]]; then
trap -- "$old; __cmdlog_preexec" DEBUG
else
trap '__cmdlog_preexec' DEBUG
fi
4. 적용 방법
rsyslog.d 하위 폴더 내용이 정상적으로 입력했는지 검증 후 이상이 없을 경우 재시작 한다.
# rsyslog 문법 체크
sudo rsyslogd -N1
# 재시작
sudo systemctl restart rsyslog
SIEM에 연동 후 사용자 입력 커멘드가 저장되고 이를통해 경보 생성 및 대응을 수행할 수 있다.

'Server > Linux' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Linux] mail 서버 설치 및 설정 (sendmail, dovecot) (0) | 2020.02.05 |
|---|---|
| [Linux] chown 명령어 설명 (0) | 2020.01.30 |
| [Linux] Umask, 특수 권한 설정 (setUID, setGID, sticky) (0) | 2020.01.30 |
| [Linux] 디렉터리, 파일 권한 설정 (0) | 2020.01.30 |
| [Linux] su, sudo 명령어 설명, 일반 사용자에게 Root 권한 부여 방법 (0) | 2020.01.29 |

공부&일상 블로그
포스팅이 좋았다면 "좋아요❤️" 또는 "구독👍🏻" 해주세요! 질문은 언제나 환영입니다😊
![[Linux] mail 서버 설치 및 설정 (sendmail, dovecot)](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdna%2FId14t%2FbtqBJ641GQj%2FAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAADBoO9eY0CinOVciFrH6q3i5zn1VwFeHhvmfbJvCqhE8%2Fimg.png%3Fcredential%3DyqXZFxpELC7KVnFOS48ylbz2pIh7yKj8%26expires%3D1772290799%26allow_ip%3D%26allow_referer%3D%26signature%3DpgRRrRRMPaUzd8Tg2dXmKYf3g1c%253D)
![[Linux] chown 명령어 설명](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdna%2FdvBIcT%2FbtqBDYygWgN%2FAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAMLkVcQtXzd6lVoi7VbMAJmR20agWYqVhdxzNd5lnDgY%2Fimg.png%3Fcredential%3DyqXZFxpELC7KVnFOS48ylbz2pIh7yKj8%26expires%3D1772290799%26allow_ip%3D%26allow_referer%3D%26signature%3DnKPlq2gpjFtJMuAsnNuV7xOK71Q%253D)
![[Linux] Umask, 특수 권한 설정 (setUID, setGID, sticky)](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdna%2FbD5G5b%2FbtqBzPXAaWN%2FAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAJyuv9Y3rU3AjWI1Rm-kZYlK53i_pSWpcvGmfTnDbi96%2Fimg.png%3Fcredential%3DyqXZFxpELC7KVnFOS48ylbz2pIh7yKj8%26expires%3D1772290799%26allow_ip%3D%26allow_referer%3D%26signature%3Dbu6lZdxBiHHzceYUjAL9k%252Fh06Hk%253D)
![[Linux] 디렉터리, 파일 권한 설정](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdna%2FdF8CUz%2FbtqBCTqyVLY%2FAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAEh8h81oPWfiB0bGYa8s1uIiYi-T6jKp8Sn2D6HqyvUG%2Fimg.png%3Fcredential%3DyqXZFxpELC7KVnFOS48ylbz2pIh7yKj8%26expires%3D1772290799%26allow_ip%3D%26allow_referer%3D%26signature%3DKAnWfTgv2m7N%252BDMYypjGxYBicgA%253D)